Adhesive Application Guide
 The Glue Doctor®
The Glue Doctor®
Ellsworth Adhesives
Adhesives vs. Stress
When considering the proper selection of an adhesive, one needs to carefully examine all factors. One of the most important considerations is the type of stress the adhesive will have to withstand. Stress is the force pulling bonded materials apart. The basic type of stresses are illustrated below.

Peel Stress
Requires a flexible substrate. Occurs as the flexible substrate is being peeled or lifted away.
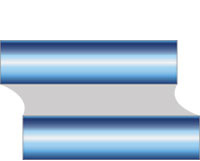
Shear Stress
Occurs as two substrates slide over eachother, with the ends of the bond resisting more than the middle.

Tensile Stress
Exerts an equal force over the entire joint, with a straight tensile stress direction. Elongation may occur.
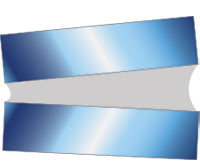
Cleavage Stress
This type of stress is concentrated at one end of a joint and occurs when a prying force is placed on the adhesive bond.

Compressive Stress
Compressive stress occurs when two substrates are squeezed or pressed together.
Area |
||
|
1 Sq. Inch = 0.00694 Sq. Feet |
1 Sq. Foot = 144 Sq. Inches |
1 Sq. Miles = 2.78784 x 10(7) Sq. Feet |
|
1 Sq. Inch = 2.491 x 10 (-10) Sq. Miles |
1 Sq. Foot = 0.111 Sq. Yards |
1 Sq. Miles = 3.098 x 10(6) Sq. Yards |
|
1 Sq. Inch = 1 x 10(6) Sq. Mils |
1 Sq. Foot = 2.2957 x 10(-5) Acres |
1 Sq. Miles = 640 Acres |
|
1 Sq. Inch = 645.16 Sq. Millimeters |
1 Sq. Foot = 3.58701 x 10(-8) Sq. Miles |
1 Sq. Miles = 258.999 Hectares |
|
1 Sq. Inch = 6.4516 Sq. Centimeters |
1 Sq. Foot = 929.03 Sq. Centimeters | 1 Sq. Miles = 2,589,988 Sq. Meters |
|
1 Sq. Inch = 0.000645 Sq. Meters |
1 Sq. Foot = 0.0929 Sq. Meters | 1 Sq. Miles = 2.58999 Sq. Kilometers |
|
|
||
|
1 Sq. Millimeter = 0.00155 Sq. Inches |
1 Sq. Centimeter = 0.155 Sq. Inches |
1 Sq. Meter = 1,550.003 Sq. Inches |
|
1 Sq. Millimeter = 1.076 x 10(-5) Sq. Feet |
1 Sq. Centimeter = 0.001076391 Sq. Feet |
1 Sq. Meter = 10.7639 Sq. Feet |
|
1 Sq. Millimeter = 1,973.5 Circular Mils |
1 Sq. Centimeter = 3.861 x 10(-11) Sq. Miles |
1 Sq. Meter = 3.861 x 10(-7) Sq. Miles |
|
1 Sq. Millimeter = 1.2732 Circular Millimeters |
1 Sq. Centimeter = 155,000 Sq. Mils |
1 Sq. Meter = 0.000247 Acres |
|
1 Sq. Millimeter = 0.01 Sq. Centimeters |
1 Sq. Centimeter = 100 Sq. Millimeters | 1 Sq. Meter = 10,000 Sq. Centimeters |
|
1 Sq. Millimeter = 1 x 10(-6) Sq. Meters |
1 Sq. Centimeter = 0.0001 Sq. Meters | 1 Sq. Meter = 1 x 10(-6) Sq. Kilometers |
|
1 Sq. Millimeter = 1.550003 x 10(9) Sq. Inches |
1 Sq. Centimeter = 15.50003 Sq. Inches | 1 Acre = 6.27264 x 10(6) Sq. Inches |
|
|
||
|
1 Sq. Kilometer = 1.07639 x 10(7) Sq. Feet |
1 Sq. Decimeter = 100 Sq. Centimeters |
1 Acre = 43,560 Sq. Feet |
|
1 Sq. Kilometer = 0.3861 Sq. Miles |
1 Sq. Decameter = 119.599 Sq. Yards |
1 Acre = 1.5625 x 10(-3) Sq. Miles |
|
1 Sq. Kilometer = 247.1054 Acres |
1 Sq. Decameter = 100 Sq. Meters |
1 Acre = 4.04686 x 10(7) Sq. Centimeters |
|
1 Sq. Kilometer = 10(10) Sq. Centimeters |
1 Sq. Decameter = 0.02471 Acres |
1 Acre = 4,046.856421 Sq. Meters |
|
1 Sq. Kilometer = 1 x 10(6) Sq. Meters |
1 Sq. Hectometer = 10,000 Sq. Meters | 1 Acre = 4.04686 x 10(-3) Sq. Kilometers |
Energy |
|
|
1 British Thermal Unit (Btu) = 251.996 Calories (g) |
1 joule (abs) = 0.0009485 British Thermal Unit (Btu) |
|
1 British Thermal Unit (Btu) = 777.649 Foot pound-force |
1 joule (abs) = 0.23901 Calories (g) |
|
1 British Thermal Unit (Btu) = 1.0751 x 10(7) Gram-force cm |
1 joule (abs) = 0.0003485 Cubic-foot atmosphere |
|
1 British Thermal Unit (Btu) = 0.000393 Horsepower-hours |
1 joule (abs) = 0.7376 Foot-pound-force |
|
1 British Thermal Unit (Btu) = 1,054.35 Joules |
1 joule (abs) = 10,197.2 Gram-force centimeter |
|
1 British Thermal Unit (Btu) = 0.2520 Kilogram-calories |
1 joule (abs) = 3.7251 x 10(-7) Horsepower-hours |
|
1 British Thermal Unit (Btu) = 0.000292875 Kilowatt-hours |
1 joule (abs) = 2.78 x 10(-7) Kilowatt-hours |
|
1 British Thermal Unit (Btu) = 1,054.35 Watt-seconds |
1 joule (abs) = 1 Watt-seconds |
Torque |
|
|
1 Newton-meter = 8.8507 Pound-force inch |
1 foot pound-force = 13,825.5 Gram-force centimeters |
|
1 Newton-meter = 0.73756 Foot pound-force |
1 foot pound-force = 5.0505051 x 10(-7) HP-hours |
|
1 Newton-meter = 10197 Gram-force centimeter |
1 foot pound-force = 0.13825495 Kilogram-force meter |
|
1 Newton-meter = 0.10197 Kilogram-force meter |
1 foot pound-force = 1.3558179 Newton-meters |
Force |
||
|
1 Oz-Force per Sq. Inch = 0.0625 Pound-Force per Sq. Inch |
1 lb-Force per Sq. Inch = 0.04448 Joules per cm |
|
|
1 Oz-Force per Sq. Inch = 9 Pound-Force per Sq. Foot |
1 lb-Force per Sq. Inch = 4.44822 Joules per Meter |
|
|
1 Oz-Force per Sq. Inch = 430.922 Newtons per Sq. Meter |
1 lb-Force per Sq. Inch = 0.453592 Kilogram-Force |
|
|
1 Oz-Force per Sq. Inch = 430.922 Pascals |
1 lb-Force per Sq. Inch = 4.44822 Newtons |
|
|
1 Oz-Force per Sq. Inch = 4.39418 Gram-Force per Sq. cm |
1 lb-Force per Sq. Inch = 444,822.166 Dynes | |
|
|
||
|
1 Newton = 1.0 Joules per Meter |
1 Kg-Force Meter = 7.233 Foot Pound-Force |
1 Dyne = 0.0010197 Gram-Force |
|
1 Newton = 0.10197 Kg-Force |
1 Kg-Force Meter = 100,000 Gram-Force cm |
1 Dyne = 1.02 x 10(-6) Kg-Force |
|
1 Newton = 0.2248089 Lbs-Force |
1 Kg-Force Meter = 9.80665 Newton-Meters |
1 Dyne = 2.248 x 10(-6) lb-Force |
|
1 Newton = 100,000 Dynes |
1 Kg-Force Meter = 0.002724 Watt-Hours |
1 Dyne = 0.00001 Newtons |
Metric |
|
|
1 Millimeter (mm) = 1 |
Millimeter (mm) = .10 |
|
1 Centimeter (cm) = 10 |
Millimeter (mm) = 1 |
|
1 Decimeter (dm) = 100 |
Millimeter (mm) = 10 |
|
1 Meter (m) = 1,000 |
Millimeter (mm) = 100 |
|
1 Kilometer (km) = 1,000,000 |
Millimeter (mm) = 100,000 |
|
Centimeter (cm) = .01 |
Decimeter (dm) = .001 Meter (m) |
|
Centimeter (cm) = .10 |
Decimeter (dm) = .010 Meter (m) |
|
Centimeter (cm) = 1 |
Decimeter (dm) = .10 Meter (m) |
|
Centimeter (cm) = 10 |
Decimeter (dm) = 1 Meter (m) |
|
Centimeter (cm) = 10,000 |
Decimeter (dm) = 1,000 Meter (m) |
Temperature |
||
|
Degrees Celsius = (Fahrenheit - 32) / 1.8 |
Degrees Fahrenheit = (1.8 x Celsius) + 32 |
|
|
Mercury Freezes |
= -40 ˚C |
= -40 ˚F |
|
Water Freezes |
= 0 ˚C |
= 32 ˚F |
|
Comfortable Room |
= 22 ˚C |
= 68 ˚F |
|
Human Body |
= 37 ˚C | = 98 ˚F |
|
Water Boils |
= 100 ˚C | = 212 ˚F |
|
Baking Oven |
= 150 ˚C | = 302 ˚F |
|
Lead Melts |
= 328 ˚C | = 622 ˚F |
Length |
||
|
1 Inch (in) = 25.4 Millimeters (mm) |
1 Foot (ft) = 304.8 Millimeters (mm) |
1 Yard (yd) = 914.4 Millimeters (mm) |
|
1 Inch (in) = 2.54 Centimeters (cm) |
1 Foot (ft) = 30.48 Centimeters (cm) |
1 Yard (yd) = 91.44 Centimeters (cm) |
|
1 Inch (in) = 0.0254 Meters (m) |
1 Foot (ft) = 0.3048 Meters (m) |
1 Yard (yd) = 0.9144 Meters (m) |
|
1 Inch (in) = 0.08333 Feet (ft) |
1 Foot (ft) = 3.048 x 10(-4) Kilometers (km) |
1 Yard (yd) = 9.144 x 10(-4) Kilometers (km) |
|
1 Inch (in) = 0.0277 Yards (yd) |
1 Foot (ft) = 12 Inches (in) | 1 Yard (yd) = 36 Inches (in) |
|
1 Inch (in) = 1.578 x 10(-5) Miles |
1 Foot (ft) = 0.000189 Miles (Statute) | 1 Yard (yd) = 5.682 x 10(-4) Miles (statute) |
|
|
||
|
1 Mile (mi) = 160,934 Centimeters |
1 Micron = 1,000 Millimicrons |
1 Millimeter (mm) = 39.37 Mils |
|
1 Mile (mi) = 1,609.344 Meters |
1 Micron = 0.001 Millimeters (mm) |
1 Millimeter (mm) = .01 Centimeters |
|
1 Mile (mi) = 1.609344 Kilometers |
1 Micron = 0.0001 Centimeters (cm) |
1 Millimeter (mm) = 0.001 Meters |
|
1 Mile (mi) = 63,360 Inches |
1 Micron = 1 x 10(-5) Meters (m) |
1 Millimeter (mm) = 1 x 10(-6) Kilometers |
|
1 Mile (mi) = 5,280 Feet |
1 Micron = 3.937 x 10(-5) Inches (in) | 1 Millimeter (mm) = 0.3937 Inches |
|
1 Mile (mi) = 0.8684 Miles (Nautical) |
1 Micron = 3.2808 x 10(-6) Feet (ft) | 1 Millimeter (mm) = 0.00328 Feet |
|
|
||
|
1 Centimeter (cm) = 393.7 Mils |
1 Meter (m) = 39,370.08 Mils |
1 Kilometer (km) = 10(+6) Millimeters (mm) |
|
1 Centimeter (cm) = 10 Millimeters (mm) |
1 Meter (m) = 1,000 Millimeters (mm) |
1 Kilometer (km) = 100,000 Centimeters (cm) |
|
1 Centimeter (cm) = 0.01 Meters (m) |
1 Meter (m) = 100 Centimeters (cm) |
1 Kilometer (km) = 1,000 Meters (m) |
|
1 Centimeter (cm) = 1 x 10(-5) Kilometers (km) |
1 Meter (m) = 0.001 Kilometers (km) |
1 Kilometer (km) = 3.937 x 10(+4) Inches (in) |
|
1 Centimeter (cm) = 0.3937 Inches (in) |
1 Meter (m) = 39.3701 Inches (in) | 1 Kilometer (km) = 3,280.84 Feet (ft) |
|
1 Centimeter (cm) = 0.03281 Feet (ft) |
1 Meter (m) = 3.28084 Feet (ft) |
1 Kilometer (km) = 1,093.61 Yards (yd) |
|
1 Centimeter (cm) = 0.01094 Yards (yd) |
1 Meter (m) = 1.0936 Yards (yd) | 1 Kilometer (km) = 0.62137 Miles (mi) |
|
1 Centimeter (cm) = 6.2137 x 10(-6) Miles |
1 Meter (m) = 0.000621 Miles (mi) |
|
Mass |
||
|
1 Ounce (oz) = 283.5 Milligrams (mg) |
1 Pound (lb) = 453.59 Grams (gr) |
1 Short Ton = 907.185 Kilograms (kg) |
|
1 Ounce (oz) = 28.35 Grams (g) |
1 Pound (lb) = 0.4536 Kilograms (kg) |
1 Short Ton = 32,000 Ounces (oz) |
|
1 Ounce (oz) = 0.0283 Kilograms (kg) |
1 Pound (lb) = 16 Ounces (oz) |
1 Short Ton = 2,000 Pounds (lb) |
|
1 Ounce (oz) = 0.0625 Pounds (lb) |
1 Pound (lb) = 0.004536 Metric Ton |
1 Short Ton = 0.89286 Tons (long) |
|
1 Ounce (oz) = 2.79 x 10(-5) Ton (long) |
1 Pound (lb) = 0.0004464 Long Ton | |
|
|
||
|
1 Long Ton = 1,016.05 Kilograms (kg) |
1 Milligram (mg) = 0.001 Grams (gm) |
1 Stone (British) = 14 Pounds (lb) |
|
1 Long Ton = 35,840 Ounces (oz) |
1 Milligram (mg) = 1x10(-6) Kilograms (kg) |
|
|
1 Long Ton = 2,240 Pounds (lb) |
1 Milligram (mg) = 3.527 x 10(-5) Ounces (oz) |
1 Decigram (dc) = 1.0 Grams (gm) |
|
1 Long Ton = 1.12 Tons (short) |
1 Milligram (mg) = 2.205 x 10(-6) Pounds (lb) |
1 Dekagram (dg) = 10 Grams (gm) |
|
|
||
|
1 Gram (gr) = 1,000 Milligrams (mg) |
1 Kilogram (kg) = 1000 Grams (gr) |
1 Ton (metric) = 1 x 10(6) Grams (gr) |
|
1 Gram (gr) = 10 Decigrams (dc) |
1 Kilogram (kg) = 0.001 Tons (metric) |
1 Ton (metric) = 1,000 Kilograms (kg) |
|
1 Gram (gr) = 0.1 Dekagrams (dg) |
1 Kilogram (kg) = 35.27396 Ounces (oz) |
1 Ton (metric) = 35,273.96 Ounces (oz) |
|
1 Gram (gr) = 0.001 Kilograms (kg) |
1 Kilogram (kg) = 2.2462 Pounds (lb) |
1 Ton (metric) = 2,204.62 Pounds (lb) |
|
1 Gram (gr) = 1x10(-6) Tons (metric) |
1 Kilogram (kg) = 0.001102 Tons (short) | 1 Ton (metric) = 1.1023 Ton (short) |
|
1 Gram (gr) = 0.03527 Ounces (oz) |
1 Kilogram (kg) = 0.00098 Tons (long) |
1 Ton (metric) = 0.98421 Ton (long) |
|
1 Gram (gr) = 0.002205 Pounds (lb) |
||
Volume |
||
|
1 Fluid Ounce (fl oz) = 29.57 Milliliters (ml) |
1 Fl. Ounce (CA) = 28.413 Milliliters (ml) |
1 Cup = 236.588 Milliliters (ml) |
|
1 Fluid Ounce (fl oz) = 0.02957 Liters (l) |
1 Fl. Ounce (CA) = 0.02841 Liters (l) |
1 Cup = 0.2366 Liters (l) |
|
1 Fluid Ounce (fl oz) = 0.0625 Pints US (p) |
1 Fl. Ounce (CA) = 0.96076 Ounces US (oz) |
1 Cup = 8 Ounces (oz) |
|
1 Fluid Ounce (fl oz) = 0.0312 Quarts US (q) |
1 Fl. Ounce (CA) = 0.00625 Gallons (gal) |
1 Cup = 0.5 Pints (p) |
|
1 Fluid Ounce (fl oz) = 0.00781 Gallons (US) |
1 Fl. Ounce (CA) = 28.413 Cubic Centimeter | 1 Cup = 0.25 Quarts (q) |
|
1 Fluid Ounce (fl oz) = 29.5735 Cubic cm |
1 Fl. Ounce (CA) = 1.7339 Cubic Inches |
1 Cup = 0.0625 Gallons (gal) |
|
1 Fluid Ounce (fl oz) = 1.80469 Cubic Inches |
||
|
|
||
|
1 Pint (US) = 473.176 Milliliters (ml) |
1 Pint (CA) = 568.26 Milliliters (ml) |
1 ml = 0.001 Liters |
|
1 Pint (US) = 0.473176 Liters (l) |
1 Pint (CA) = 0.56826 Liters (l) |
1 ml = 0.035195 Ounces CA (oz) |
|
1 Pint (US) = 16 Ounces US (oz) |
1 Pint (CA) = 20 Ounces CA (oz) |
1 ml = 0.0338 Ounces US (oz) |
|
1 Pint (US) = 0.5 Quarts US (qt) |
1 Pint (CA) = 0.125 Gallons (gal) |
1 ml = 0.00219 Gallons CA (gal) |
|
1 Pint (US) = 0.125 Gallons US (gal) |
1 Pint (CA) = 568.261 Cubic Centimeters |
1 ml = 0.000264 Gallons US (gal) |
|
1 Pint (US) = 473.1765 Cubic Centimeter |
1 Pint (CA) = 34.68 Cubic Inches |
1 ml = 1.0 Cubic Centimeter |
|
1 Pint (US) = 28.875 Cubic Inches |
1 ml = 0.06102 Cubic Inches |
|
|
|
||
|
1 Gallon (US) = 3.77854 Liters (l) |
1 Gallon (CA) = 4.546 Liters (l) |
1 Liter (l) = 1,000 Milliliters (ml) |
|
1 Gallon (US) = 128 Ounces US (oz) |
1 Gallon (CA) = 160 Ounces CA (oz) |
1 Liter (l) = 35.195 Ounces CA (oz) |
|
1 Gallon (US) = 8.337 lbs Water (62 ˚F) |
1 Gallon (CA) = 153.722 Ounces US (oz) |
1 Liter (l) = 33.81402 Ounces US (oz) |
|
1 Gallon (US) = 0.83267 Gallons CA (gal) |
1 Gallon (CA) = 10.0092 lbs Water (62 ˚F) |
1 Liter (l) = 1.7598 Pints CA (p) |
|
1 Gallon (US) = 3,785.41 Cubic Centimeters |
1 Gallon (CA) = 1.2009 Gallons US (gal) | 1 Liter (l) = 2.1134 Pints US (p) |
|
1 Gallon (US) = 231 Cubic Inches |
1 Gallon (CA) = 277.419 Cubic Inches |
1 Liter (l) = 0.8799 Quarts CA (q) |
|
1 Gallon (US) = 0.15556 Cubic Feet |
1 Gallon (CA) = 0.1605 Cubic Feet | 1 Liter (l) = 1.0567 Quarts US (q) |
|
|
||
|
1 Cubic cm = 0.001 Liters (l) |
1 Cubic Inch = 0.01639 Liters (l) |
1 Liter (l) = 0.21997 Gallons CA |
|
1 Cubic cm = 0.03519 Ounces CA (oz) |
1 Cubic Inch = 0.57674 Ounces CA (oz) |
1 Liter (l) = 0.26417 Gallons US |
|
1 Cubic cm = 0.03381 Ounces US (oz) |
1 Cubic Inch = 0.55411 Ounces US (oz) |
1 Liter (l) = 1000 Cubic Centimeters |
|
1 Cubic cm = 0.00022 Gallons CA (gal) |
1 Cubic Inch = 0.00360 Gallons CA (gal) |
1 Liter (l) = 0.001 Cubic Meters |
|
1 Cubic cm = 0.00026 Gallons US (gal) |
1 Cubic Inch = 0.00433 Gallons US (gal) | 1 Liter (l) = 61.0237 Cubic Inches |
|
1 Cubic cm = 63.366 Pounds of Water |
1 Cubic Inch = 0.03609 Pounds of Water |
1 Liter (l) = 0.00131 Cubic Yards |
Viscosity |
|
|
Viscosity: The measure of the resistance of a fluid to flow. Centipoise: Water is the standard by which all fluids are measured (shown as cps). Water is 1 cps at 70˚F. Thixotropic: This describes a fluid that is gel-like (toothpaste) at rest, but will move with |
|
|
Water at 70˚F |
1 to 3 Centipoise (cps) |
|
Blood |
10 Centipoise (cps) |
|
Ethylene Glycol |
15 Centipoise (cps) |
|
Motor Oil (SAE 10) |
50 Centipoise (cps) |
| Corn Oil | 65 Centipoise (cps) |
| Maple Syrup | 150 Centipoise (cps) |
| Motor Oil (SAE 40) | 250 Centipoise (cps) |
| Motor Oil (SAE 60) | 1,000 Centipoise (cps) |
| Honey | 2,000 Centipoise (cps) |
| Molasses | 5,000 Centipoise (cps) |
| Chocolate Syrup | 10,000 Centipoise (cps) |
| Ketchup | 50,000 Centipoise (cps) |
| Peanut Butter | 150,000 Centipoise (cps) |
| Lard | 1,000,000 Centipoise (cps) |
Note: All viscosities are approximate at standard room temperature. Values will be higher at colder temperatures and lower at elevated temperatures.
Bead LengthChart for methacrylates, epoxies, and silicones |
||||
|
1/4" Wide Bead |
3/8" Wide Bead |
1/2" Wide Bead |
5/8" Wide Bead |
|
|
50 ml |
124 Inches |
56 Inches |
30 Inches |
20 Inches |
|
300 ml |
740 Inches |
335 Inches |
180 Inches |
120 Inches |
|
380 ml |
945 Inches |
420 Inches |
230 Inches |
151 Inches |
|
400 ml |
992 Inches | 448 Inches |
240 Inches |
160 Inches |
|
1 Pound |
1,073 Inches | 477 Inches |
265 Inches |
172 Inches |
|
1 Gallon |
9,450 Inches | 4,200 Inches |
2,360 Inches |
1,510 Inches |
Adhesive Usage Chart for Cyanoacrylates and Anaerobics |
||||||
|
Gap (Inches) |
1 Sq. Inch |
2 Sq. Inch |
4 Sq. Inch |
8 Sq. Inch |
10 Sq. Inch |
20 Sq. Inch |
|
.015 Inches |
1,940 Pieces |
946 Pieces |
475 Pieces |
240 Pieces |
185 Pieces |
95 Pieces |
|
.010 Inches |
2,955 Pieces |
1,420 Pieces |
710 Pieces |
355 Pieces |
270 Pieces |
140 Pieces |
|
.005 Inches |
5,915 Pieces |
2,840 Pieces |
1,420 Pieces |
710 Pieces |
565 Pieces |
285 Pieces |
|
.002 Inches |
14,190 Pieces | 7,100 Pieces |
3,550 Pieces |
1,655 Pieces |
1,410 Pieces |
705 Pieces |
Note: Parts per pound of cyanoacrylate are based on gap (in inches) times bond area (in square inches).
|
Centipoise of Cyanoacrylate |
Drops per Ounce Bottle |
Drops per Pound Bottle |
|
5 cps |
1,097 |
17,552 |
|
45 cps |
926 |
14,816 |
|
100 cps |
904 |
14,464 |
|
500 cps |
641 | 10,256 |
|
1000 cps |
549 |
8,784 |
|
2400 cps |
385 | 6,160 |
|
3000 cps |
356 |
5,696 |
|
5000 cps |
313 | 5,008 |
Note: Drops per pound of cyanoacrylate are based on free-falling drops at room temperature. Use as approximate.
Weight and Properties of Common Materials |
||||
| Material |
Specific Gravity |
Weight (lbs per cu. ft.) |
Weight (kg per cu. meter) |
|
|
ABS |
1.05 |
65.5 |
1,050.0 |
|
|
Acetone |
0.79 |
49.3 |
790.0 |
|
|
Epoxy |
1.26 |
78.3 |
1,255.0 |
|
|
Ethylene Glycol |
1.11 | 69.5 |
1,114.0 |
|
|
HDPE |
0.96 | 59.8 |
958.5 |
|
|
LDPE |
0.92 | 57.7 |
924.5 |
|
|
Methyl Chloride |
0.99 | 61.8 |
990.0 |
|
|
Nylon (Type 6) |
1.13 | 70.5 |
1,130.0 |
|
|
Nylon (Type 6/6) |
1.14 | 71.2 |
1,140.0 |
|
|
Polycarbonate |
1.20 | 74.9 |
1,200.0 |
|
|
Polyethylene |
1.70 | 106.1 |
1,700.0 |
|
|
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) |
1.31 | 81.8 |
1,310.0 |
|
|
Polyethyleneterephthalate (PET) |
1.35 | 84.0 |
1,345.0 |
|
|
Polyester (Cast) |
1.25 | 78.0 |
1,250.0 |
|
|
Polypropylene (PP) |
0.91 | 56.5 |
905.0 |
|
|
Polystyrene (PS) |
1.05 | 65.5 |
1,050.0 |
|
|
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
1.30 | 81.2 |
1,300.0 |
|
|
Toluene |
0.87 | 54.6 |
870.0 |
|
|
Trichlorethylene |
1.47 | 91.8 |
1,470.0 |
|
|
Water (Pure) |
1.00 | 62.4 |
999.6 |
|
|
Water (Sea) |
1.03 | 64.08 |
1,026.5 |
|
Common Adhesives
Rating: 1 = Poor 2 = Best
Acrylics
Commonly supplied either as a two component adhesive in a variety of ratios (1:1, 4:1, or 10:1) or as a single component with an applied primer. The dual component is used mainly for structural bonding of porous and non- porous substrates and is oil, gas, water, and salt resistant. More common uses are structural bonds of fiberglass, composites, ABS, PVC, etc. The automotive industry is a common user whereas the single component material is generally used in the speaker magnet bonding industry. Acrylics tend to be very good gap filling, fast curing adhesives that lend themselves well to automated or semi-automated production. These adhesives cure by way of an exothermic reaction and the cost of using these adhesives is medium to high depending on the bead thickness used.
Production = 9 Cost = 6 - 7 User Friendly = 8 Odor = 8 Strength = 10
Acrylonitrile (Rubber Cement)
Commonly used in schools to bond paper and cardboard substrates. Applied as a single component which cures by way of solvent release, it has limited potential as a production adhesive.
Production = 1 Cost = 2 User Friendly = 8 Odor = 8 Strength = 3
Aliphatic Resin (Yellow Glue)
Commonly used in the woodworking industry to bond a variety of wood products. This adhesive is very strong, moisture resistant (not waterproof), and has a high resistance to solvents and heat. This is a single component adhesive, non-toxic, non-flammable, and non-staining.
Production = 5 Cost = 4 User Friendly = 8 Odor = 2 Strength = 9
Contact Cement
Commonly supplied for bonding laminated assemblies such as counter tops and veneers. This adhesive is a single component and is usually applied to both substrates and then held together under high pressure. This adhesive can be purchased either with a solvent carrier, which is flammable, or the newer water-based cements, which is some instances can be just as fast setting as the solvented versions.
Production = 5 Cost = 3-6 User Friendly = 8 Odor = 3 - 6 Strength = 5
Cyanoacrylate Ester
This adhesive is supplied as a single component adhesive that cures by way of moisture. The thinner the bead displacement between substrates and the more residual moisture on the substrates equals faster cure times. These cure times (green strength) may be between 10 seconds and 2 minutes. Production guidelines as to substrates, fixturing, ambient humidity, and bead size all are important in ensuring the most success from this adhesive. Cyanoacrylates tend to bond rubbers very well, as well as Nylon, PVC, EPDM, and most plastics. Some hard to bond plastics such as polypropylene can be bonded with cyanoacrylates using some of the newer primers.
Production = 9 Cost = 6 User Friendly = 8 Odor = 3 Strength = 9
Epoxy
This adhesive is a very common commodity with a vast array of uses. Epoxies can be used as a single component heat cured product to a dual component adhesive with many different additives. The uses seem to be unlimited for epoxies and as technology grows so does the use for these adhesives. Epoxies range in cure times from a very fast 3 minutes to a slow cure of 24 hours with hardness and elongation covering a very wide range. As a true engineered adhesive, epoxies can be altered to fit nearly any manufacturing need for adhesives.
Costs and packaging are determined by the end use of this adhesive. Common uses are potting compounds, metal bonding, structural bonding, and consumer packaged general-purpose adhesives.
Production = 9 Cost = 5 - 8 User Friendly = 8 Odor = 3 - 6 Strength = 6 - 9
Hot Melt Glue
Hot melt adhesives form a large segment of the adhesive industry and are supplied as a single component material packaged in sticks, chicklets, pillows, slugs, pails, and drums. These adhesives can be used in a wide variety of applications ranging from labeling to structural automotive bonding to consumer craft glue. The more common hot melts are EVA and PVA and are generally used for medium strength applications while PURs (Polyurethane Hot Melts) and polyamides should be used for any structural applications.
The common applications include foam bonding, labels, automotive applications including headliners, seats, dashboard, and headlamp assemblies. Application methods can include hot melt glue guns using simple sticks to complicated roll coating dispensing systems for applying uniform thickness.
Production = 9 Cost = 2 - 5 User Friendly = 6 Odor = 3 Strength = 4 - 9
Latex Cement
Commonly used in paper items such as wallpaper and bonding of fabrics. This adhesive is a low cost, low strength, water resistant glue with a high degree of flexibility when cured.
Production = 7 Cost = 2 - 3 User Friendly = 5 Odor = 3 Strength = 2
Silicones
Generally used as a sealer or caulking compound, this product also has good adhesion characteristics. Silicones have an overall moderate strength on most porous to non-porous substrates and generally do not wet out well on polypropylenes or high olefin plastics. Silicones are also regarded as a very good waterproof adhesive that can withstand very low to very high temperatures (-40 to +600 ˚F). The downfall of silicones is the very long cure time of 2 hours to 48 hours depending on the residual humidity. The secondary use of silicones is as a two component mold-making product. Silicones offer superior performance with their flexibility and different cure catalysts available.
Production = 2 Cost = 2 - 3 User Friendly = 4 Odor = 8 Strength = 4
Ultraviolet Adhesives
This branch of the adhesive world uses acrylics, epoxies, and urethanes to achieve the desired results both with the substrates and production process. UV cured acrylics are generally used for glass bonding while UV urethanes and epoxies are used in the electronic industry to coat circuit boards. As UV lamps become cheaper, safer, and easier to use, the use of ultraviolet adhesives will increase.
Production = 7 Cost = 8 User Friendly = 6 Odor = 6 Strength = 8
Common Adhesive Questions
- What substrate are you bonding?
- Is one substrate flexible while the other is rigid?
- Do we have gap filling issues to contend with? Is there a slip fit or a press fit?
- What is the processing time the adhesive needs to work with, to match the manufacturing parameters set out on the process?
- Is there a concern with adhesive odors?
- How will we apply the adhesive? Automated or semi-automated?
- Is there a budget on both equipment and adhesives used?
- How many operators?
- How do we store the adhesives on line?
- Do we need to match an automotive specification to use the adhesive? What testing needs to be done, such as PPAP, FMEA, or process flow documents?
- Do we have any environmental constraints while using this adhesive?
- How many parts are we processing per hour, day, month, or year?
Basic Bonded Joints
![]()
Simple Lap Joint
![]()
Tapered Lap Joint
![]()
Scarf Joint
![]()
Butt Joint
![]()
Strap Joint
![]()
Double Strap Joint

Tapered Double Strap Joint

Double Lap Joint
![]()
Stepped Lap Joint
Adhesives Terminology
Adhesive Failure
The loss of adhesion between the adhesive and the substrates bonded. This would look as though the adhesive had peeled clean off of one side of the substrate and left adhesive on the other.
Bond Strength
The amount of adhesion between the bonded substrates usually measured in pounds per square inch. The usual test is to bond 1” x 4” coupons with a 1” overlap and pull in a tensile test.
Centipoise
The measure of flowability of a liquid, a unit of viscosity. Water is measured at 1cps (Centipoise). See chart.
Cohesive Failure
Loss of adhesion due to adhesive tear or rupture, leaving adhesive on both substrates.
Cure
To change the physical properties of a material by chemical reaction, which may be condensation, polymerization, or vulcanization; usually accomplished by the action of heat, moisture, and/or catalysts alone or in combination with or without pressure.
Cure Time
The amount of time it takes for an adhesive to come to full strength.
Gel Time
The time it takes (usually in minutes), for a specific amount of mixed resin and hardener to become unworkable (gelled).
Green Time (open time)
Open time is the time between application and solidification of the adhesive. During the open time, it is still possible to position parts while being careful not to overlap the open time with the fixturing time of the adhesive. This will cause an interruption in the curing process and may lead to a less than adequate bond strength.
Peel Strength
The amount of force required to peel a material off of a substrate.
Shear Strength
The maximum shearing force, per unit area (sq. in.), an adhesive bond will endure before failure. Usual test is lap shear coupons 1” x 4”.